经典的多线程的模型之一,生产者消费者模型,了解一下
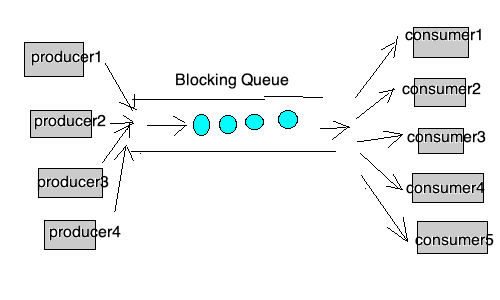
生产者和消费者共用一段内存空间,生产者向共享存储区中添加产品,消费者从其中取走产品,当存储区域为空的时候,消费者阻塞,当存储区满的时候,生产者阻塞。
runloop、looper、eventloop这些是不是另一类生产者消费者的应用呢?
实现方式有很多种,比如使用阻塞队列BlockingQueue,并发与容量控制都已经封装在容器里了
下面练习一下 wait 和 notifyAll的方法实现方式(并发与容量控制没有封装在缓冲区,就由生产者消费者完成)
import java.util.ArrayDeque;
import java.util.Queue;
public class ProducerConsumer2 {
static class MyBlockingQueue<E>{
private Queue<E> queue = null;
private int limit;
public MyBlockingQueue(int limit){
this.limit = limit;
queue = new ArrayDeque<E>(limit);
}
public synchronized void put(E e) throws InterruptedException {
while(queue.size() == limit){
wait();
}
queue.add(e);
notifyAll();
}
public synchronized E take() throws InterruptedException {
while(queue.isEmpty()){
wait();
}
E e = queue.poll();
notifyAll();
return e;
}
}
static class Producer extends Thread {
MyBlockingQueue<String> queue;
public Producer(MyBlockingQueue<String> queue){
this.queue = queue;
}
@Override
public void run(){
int num = 0;
try{
while(true){
String task = String.valueOf(num);
queue.put(task);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " produce task " + task);
num++;
Thread.sleep((int)(Math.random()*100));
}
}catch(InterruptedException e){
}
}
}
public static class Consumer extends Thread {
MyBlockingQueue<String> queue;
public Consumer(MyBlockingQueue<String> queue){
this.queue = queue;
}
@Override
public void run(){
try{
while(true){
String task = queue.take();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " Consumer task " + task);
Thread.sleep((int)(Math.random()*100));
}
}catch(InterruptedException e){
}
}
}
public static void main(String args[]){
MyBlockingQueue queue = new MyBlockingQueue<String>(10);
new Producer(queue).start();
new Consumer(queue).start();
}
}
while是为了刚刚抢到锁到线程再一次循环判断是否满足继续执行下去的条件,notifyAll主要是解决可能出现的线程死锁的情况,如果用notifyAll
这里使用while包裹住一段代码,倒是让我想起了宏里的用法
###
###
待补充…